Table of Contents
Through the years, newborn circumcision has been held as a sacred tradition and a custom in various communities. The procedure involves the foreskin at the penis’ head being surgically extracted.
Although hygiene, personal preference, and customs are reasons for this procedure, religions have a substantial impact. This article will explore religious perspectives, examining their significance and interpretation among different faiths.
Newborn Circumcision in Judaism
Historical and Scriptural Context
- Newborn circumcision is an agreement between God and Abraham, as chronicled in the Torah (Genesis 17:10–14). It manifests the religious and cultural significance of the procedure.
- Abraham requires that all males, including himself, undergo circumcision. This manifests his commitment to the covenant.
Symbolism and Ritual
- Among the Jews, circumcision is a divine agreement between God and his
 people. It’s carried out on the eighth day after the birth of the infant.
people. It’s carried out on the eighth day after the birth of the infant.
Contemporary Views
- Newborn circumcision is customarily practiced among the Jews.
- Being a religious responsibility, it is regarded as a core factor of Jewish identity.
Jewish parents view newborn circumcision as a way to affirm their child’s connection to their heritage and community.
- There are debates and varying perspectives within Judaism. There are arguments to modify the procedure to prioritize the infant’s well-being, such as using anesthesia or less invasive techniques.
- In modern times, some groups raise the relevance of newborn circumcision. They stress that it should be a personal decision.
Medical and Health Views
- Despite its religious practice, newborn circumcision offers potential health benefits.
- Newborn circumcision reduces the risk of certain diseases, such as UTIs and STIs.
- The benefits of the procedure vary depending on the medical viewpoint.
Legal and Ethical Views
- Several countries recognize circumcision as a fundamental liberty of religion in Judaism.
- Ethical considerations are brought out since infant circumcision is carried out without expressed consent.
- Presently, debates are still ongoing about striking a balance between parental rights, the child’s well-being, and religious freedom.
Newborn Circumcision in Islam
Circumcision is regarded as a significant and strongly encouraged custom in Islamic culture. This religious ceremony has an extensive background and encompasses various viewpoints that enhance its value in the Islamic belief system.
Beginnings of Islam
Circumcision, in Islam, began when Prophet Muhammad underwent the procedure and told his people to follow. It’s not stated in the Quran, but it’s assumed that the Prophet has strong beliefs about circumcision.
Circumcision is not Mandatory
Circumcision is not required but is highly encouraged. The prevalence of circumcision across Muslim-majority countries highlights its cultural and religious importance.
Circumcision is Purity
Circumcision is regarded as a fundamental human instinct. It’s seen as a means of body cleansing and a commitment to follow the principles laid out by the Prophet. It signifies the removal of impurities and the embrace of cleanliness.
The concept of purity is one of the main reasons for circumcision in Islam. Muslims believe that circumcision helps to maintain cleanliness, reduce the risk of infection, and promote good health.
It is believed that circumcision enhances physical cleanliness, facilitates better genital hygiene, and prevents the accumulation of smegma, a substance that can lead to infections if not properly cleaned
Circumcision is a Natural Disposition
Another perspective is the concept of fitnah. Muslims view circumcision as an act that conforms to the natural disposition and creation of human beings. It is believed that all individuals are born with an innate inclination toward Islam.
Circumcision is a Rite of Passage
Circumcision is a traditional ritual that signifies the journey from adolescence to maturity for male children. It symbolizes their inclusion in the Islamic religion and their vow to uphold its beliefs and principles.
The procedure is carried out publicly, where loved ones gather to observe the ceremony. This communal aspect reinforces the sense of unity and shared identity among Muslims.
Circumcision serves as a rite of passage. It marks the young boys’ transition from childhood to adulthood. It symbolizes their initiation into the Islamic faith as well as their commitment to upholding its values.
Circumcision Timing Varieties
Circumcision traditions and rituals within the Muslim world vary in timing and methods due to their diverse nature. Some perform circumcision shortly after birth, while others do it during childhood or even later in life.
Age Preferences for Circumcision Among Muslim Families and Cultures
The age at which boys are circumcised in Muslim families can vary significantly, influenced by various factors such as family traditions, regional practices, and religious interpretations.
Factors Influencing Age Variation
- Family Traditions: Each family may hold unique customs passed down through generations, impacting when they choose to perform circumcision.
- Regional Practices: Cultural norms in different countries can play a crucial role. For instance, in some regions, it is common to circumcise boys shortly after birth, while in others, it might align with particular life stages.
- Religious Interpretations: Subsets within Islam may have distinct guidelines or preferred ages for circumcision.
Common Age Ranges
- Early Circumcision:
- Some families opt to circumcise their sons within the first week of birth. This practice can be intertwined with regional customs or specific religious beliefs.
- Childhood Circumcision:
- Many Muslim families prefer to perform the rite when the child is around seven years old. This age is often seen as a middle ground, balancing religious traditions with medical considerations.
- Circumcision at Puberty:
- It is also not unusual for families to wait until the boy approaches puberty. This timing can be influenced by interpretations of religious texts that suggest circumcision should be done before reaching full maturity.
Understanding these variations highlights the rich tapestry of cultural and religious practices within the Muslim community. The decision about the timing of circumcision can therefore be a deeply personal one, reflecting a blend of ancestral tradition, societal norms, and religious doctrine.
Circumcision Upholds a Child’s Safety
Islamic teachings prioritize the child’s well-being and safety throughout the procedure. Only medical professionals should carry out safe practices under suitable medical conditions. Safety is of the utmost importance.
It’s recommended that parents seek medical assistance and practice good hygiene if they decide to have their newborn circumcised.
How Circumcision Symbolizes the Covenant Between Allah and Abraham
Circumcision is a practice deeply rooted in religious tradition, particularly within Islam and Judaism, symbolizing a sacred covenant. This ritual’s origins trace back to a pivotal moment in religious history: the covenant between Allah and the prophet Abraham.
The Divine Covenant
Allah made a profound promise to Abraham, vowing that his descendants would be as numerous as the grains of sand on a beach and that he would become the father of many nations. To signify this everlasting covenant, Allah instructed Abraham to circumcise every newborn male within his lineage.
A Physical and Spiritual Mark
Circumcision serves as a physical manifestation of this divine agreement. It’s not merely a medical procedure but a spiritual act that reinforces a commitment made by Abraham and his descendants to uphold their faith and devotion to Allah.
Perpetuating the Tradition
This rite has transcended generations and is still observed today. Each circumcision is a reaffirmation of commitment to the covenant, reminding believers of their historical and spiritual roots. Through this act, families continue to honor the promises made between Allah and Abraham, ensuring that their faith remains an integral part of their identity across the ages.
What Reasons Does Islam Provide for the Practice of Circumcision?
Islam marks circumcision as an important practice primarily rooted in the teachings and traditions of Prophet Muhammad, known as the Sunnah. Although the Quran does not explicitly mention circumcision, it is considered a religious requirement for males based on these authentic traditions.
Reasons Highlighted in Islamic Teachings:
- Cleanliness and Purification: One of the foremost reasons espoused by Islamic doctrine is the significance of hygiene. Muslims are required to maintain cleanliness, particularly before engaging in prayers. Circumcision aids in this by removing the foreskin, which can harbor traces of urine if not cleaned properly.
- Ritual Purity: After using the toilet, Islam mandates thorough cleaning to ensure no urine remains on the body. The prepuce (foreskin) can potentially trap urine, posing a challenge to maintaining this level of cleanliness. By removing the foreskin, circumcision thus mitigates the risk of such impurities, facilitating easier and more effective hygiene.
In essence, the procedure aligns with the broader Islamic emphasis on physical and spiritual cleanliness, ensuring that followers can maintain the required state of purification for their daily prayers and rituals. This practice underscores the religion’s holistic approach to health and devotion.
The Local Infection Prevention Benefits of Circumcision in Islam
Circumcision, an important practice in Islam, offers notable health benefits, particularly in preventing local infections in the genital area. Here’s how:
- Reduced Risk of Infections: The foreskin can create a moist environment conducive to bacterial growth, potentially leading to infections. Removing it can significantly lower the risk of such infections.
- Prevention of Foreskin Tightening: Over time, infections underneath the foreskin can lead to its tightening, a condition known as phimosis. This can cause pain and discomfort, but circumcision eliminates this issue early on.
- Long-term Health Benefits: Chronic infections linked to an intact foreskin can escalate into more serious health problems. Early circumcision can prevent these complications, ensuring better long-term genital health.
By opting for circumcision, Islamic tradition not only fulfills a religious mandate but also offers a practical health benefit by minimizing the risk of local infections and associated complications.
Circumcision in Christianity
Christianity is a diverse religion, encompassing numerous denominations and interpretations. Therefore, Christian communities have different beliefs regarding circumcision, distinct from Judaism and Islam, where it holds more importance.
Notably, the Christian faith doesn’t explicitly command or endorse circumcision based on New Testament teachings.
The issue of circumcision gained attention in the early Christian church when debates arose about the necessity of circumcision for Gentile non-Jewish converts. Apostle Paul asserted that belief in Jesus Christ was the crucial factor that justifies circumcision.
Supporting his stance, he emphatically states, “For in Christ Jesus, neither circumcision nor uncircumcision has any value. The only thing that counts is faith expressing itself through love.”
Numerous Christian groups, especially those inclined toward liberalism or Protestantism, don’t endorse circumcision as a religious rite based on their understanding of the scriptures. They consider it a parental decision rather than a religious duty.
Alternatively, certain Christian groups that have strong connections to Judaism or the Old Testament observe circumcision as a sacred ritual. These groups perceive the act as an agreement between God and His followers, akin to the Jewish interpretation.
Some groups contend that as Jesus was born and raised in a Jewish community, he most likely would have undergone circumcision as per tradition. Accordingly, some devout Christian parents choose this custom to honor their faith heritage.
The significance and religious validation of circumcision vary among different Christian communities. Certain individuals view it as a customary routine rather than a divine responsibility. Alternative believers see it as a representation of their loyalty and devotion.
Circumcision in Other Religions
Apart from Judaism and Islam, circumcision remains a crucial aspect to study in terms of other significant religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, and Jainism. Each of these religions has its own distinct beliefs and approaches toward circumcision.
Hinduism: Circumcision is not a Religious Obligation
Hinduism, one of the oldest religions worldwide, doesn’t require circumcision. It emphasizes cleanliness and purity, with some Hindu families opting for male circumcision for hygiene reasons. It’s not an obligation but a personal determination.
Buddhism: Circumcision is not a Religious Ritual
In the 6th century BCE, Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha) founded Buddhism, which holds the belief that circumcision isn’t favorable. The religion’s main goal is to lessen suffering and achieve enlightenment through ethical conduct, meditation, and mindfulness.
According to Buddhism, circumcision isn’t considered a religious ritual or an aspect of spiritual growth.
Sikhism: Circumcision is not a Sacred Ritual.
Guru Nanak Dev Ji founded Sikhism in Punjab, India, in the 15th century. Their values are belief in a single deity and treating all individuals equally. Despite the prevalence of circumcision, they neither impose it as a sacred rite nor view it as an advancement.
The Guru Granth Sahib, an essential scripture of this religion, doesn’t advocate its practice.
Jainism: Circumcision is not Part of their Tradition
Jainism is an ancient Indian religion that was founded in the sixth century BCE by Mahavira. It also opposes circumcision. They promote non-violence, called ahimsa, and compassion towards all living beings.
Jains believe in purifying the soul through righteous conduct and spiritual practices. Circumcision isn’t considered a religious requirement or a tradition. Jain rituals and practices focus on self-discipline, meditation, and the path of non-attachment.
Practices within religious communities vary. Some individuals opt to circumcise their children for personal reasons. While religious perspectives provide a general understanding of circumcision within these traditions, individual beliefs and practices still differ.
African Religion: Circumcision without any Cultural Significance
Significance
A significant number of African traditional religions and ethnic groups practice circumcision for non-religious reasons. However, significance and timing still vary.
This perspective has been practiced dating back in history in sub-Saharan Africa, the aboriginal Australasians, the Aztecs, Mayans, Eastern Indonesia, and the Pacific Islands.
Ancient Egypt: Circumcision was practiced among ancient Semitic people, including Egyptians.
Newborn circumcision has remained prevalent in many societies globally. Efforts to ban or abolish the practices have been met with resistance.
For example, in West African traditional societies, newborn circumcision is medicalized and performed in infancy without any particular conscious cultural significance.
To say it all, the practice of newborn circumcision has endured various controversies. Opponents question the extent of the documented benefits, citing the potential psychological side effects.
Respect Varying Religious Beliefs on Newborn Circumcision
Newborn circumcision carries different religious significance among faith traditions. For Jews, it symbolizes the covenant between God and the Jewish people. In Islam, it’s seen as a recommended practice based on the example of the Prophet Muhammad.
However, Christianity doesn’t consider newborn circumcision a central religious requirement. Understanding religious perspectives is crucial for appreciating the significance of newborn circumcision within different cultures and religions.
Omega Pediatrics recommends that it’s essential to approach discussions surrounding circumcision with sensitivity, respect for religious beliefs, and an understanding of the diverse perspectives that shape this practice.
FAQ
Why is newborn circumcision significant in Judaism?
Newborn circumcision is significant in Judaism as it symbolizes the covenant between God and the Jewish people, established with Abraham in the Torah. It’s considered a religious responsibility and a core factor of Jewish identity.
What are some medical benefits of newborn circumcision?
Newborn circumcision offers potential health benefits such as reduced risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, the benefits vary depending on medical viewpoints.
How does Islam view newborn circumcision?
In Islam, circumcision is highly encouraged but not mandatory. It is seen as a means of maintaining cleanliness and purity, following the example of Prophet Muhammad. Circumcision is considered a natural disposition and a rite of passage into adulthood.
What is Christianity’s stance on newborn circumcision?
Christianity’s stance on newborn circumcision varies among denominations. While some groups observe it as a sacred ritual, others, particularly those inclined toward liberalism or Protestantism, view it as a parental decision rather than a religious duty.
How do other religions, such as Hinduism and Buddhism, view newborn circumcision?
In religions like Hinduism and Buddhism, newborn circumcision is not a religious obligation or ritual. It’s often considered a personal choice rather than a religious requirement. Each religion emphasizes different aspects of spirituality and religious practice.

 people. It’s
people. It’s 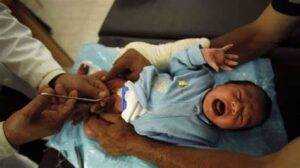
 Significance
Significance 

