Melanoma: Not Just an Adult Problem
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that, although rare, can affect children. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a cancer that begins in the melanocytes, the cells that produce the skin pigment known as melanin.
Signs: What to Look For
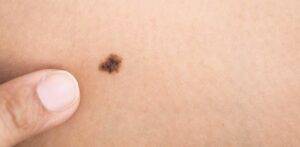
- Changing Moles: In size, shape, or color.
- New Growths: Especially if they look different from other moles.
- Itching or Bleeding: From an existing mole.
Causes: The Risk Factors
- Sun Exposure: UV radiation is a significant risk factor.
- Genetics: Family history can play a role.
- Skin Type: Fair skin is more susceptible.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Biopsy: To confirm the diagnosis.
- Surgery: To remove the melanoma.
- Additional Therapies: Like chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Melanoma in Children: An Often Overlooked Concern
While melanoma is commonly associated with adults, it is crucial to recognize that children can also be affected by this serious form of skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an increase in reported cases of melanoma among the pediatric population, making it imperative for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to be vigilant about early detection and intervention.
Recognizing Melanoma in Children
Identifying melanoma in children requires a keen eye and awareness of potential signs. Children may not always communicate changes in their skin, so parents should actively monitor for any unusual developments. The key signs to look for include:
Unusual Moles
Much like in adults, changing moles can be indicative of melanoma in children. Parents should be attentive to any alterations in the size, shape, or color of existing moles.
New Growths
The appearance of new growths, especially those that differ significantly from other moles, should raise concern. Parents should take note of any unfamiliar spots on their child’s skin and promptly consult a healthcare professional if any abnormalities are observed.
Itching or Bleeding
If an existing mole begins to itch or bleed, it could be a sign of melanoma. While not every case of itching or bleeding is linked to cancer, it is essential to address such changes promptly to rule out potential risks.
Understanding the Risk Factors in Children
While the risk factors for melanoma in children may align with those in adults, some unique considerations apply to the pediatric population:
Limited Sun Exposure
Contrary to the common belief that melanoma is solely linked to excessive sun exposure, some cases in children have been reported with minimal sun exposure. This underscores the importance of considering other risk factors and genetic predispositions.
Genetic Influences
A family history of melanoma can elevate the risk for children. Understanding the family’s medical history, especially regarding skin cancer, aids in early identification and preventive measures.
Skin Type and Susceptibility
Fair skin has long been associated with an increased risk of melanoma. Parents of fair-skinned children should be particularly vigilant and proactive in monitoring their child’s skin health.
Pediatric Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies
Diagnosing melanoma in children often involves similar procedures to those in adults. Early detection remains pivotal for successful outcomes:
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy is a definitive step in confirming the diagnosis of melanoma in children. Dermatologists may opt for various biopsy techniques, such as excisional or incisional biopsies, depending on the suspected severity of the lesion.
Surgical Intervention
As with adult cases, surgery is a primary treatment modality for pediatric melanoma. Surgeons aim to remove the cancerous cells, and the extent of the procedure depends on the stage and location of the melanoma.
Emerging Therapies for Children
In addition to surgical interventions, pediatric oncologists explore evolving therapeutic options such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy. These treatments aim to target cancer cells and boost the body’s immune response, offering new hope for improved outcomes in pediatric melanoma cases.
The Role of Prevention and Education
Preventive measures and education are paramount in addressing pediatric melanoma. Parents should prioritize:
Sun Safety
Educating children about the importance of sun safety, including the regular application of sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sunlight hours, can significantly reduce the risk of melanoma.
Regular Skin Checks
Encouraging routine skin examinations at home and regular dermatologist visits can contribute to early detection. Empowering children to be aware of changes in their own skin fosters a proactive approach to health.
Ongoing Research and Collaborative Efforts
The landscape of pediatric melanoma research is continually evolving, with scientists and medical professionals dedicated to advancing our understanding of this complex disease. Ongoing research aims to unravel the intricacies of melanoma development in children, seeking more targeted therapies and improved prognostic indicators.
Genetic Insights
With the growing recognition of genetic factors in pediatric melanoma, researchers are delving deeper into the molecular underpinnings of the disease. Genetic testing and genomic studies are shedding light on specific gene mutations that may predispose children to melanoma, opening avenues for tailored treatment approaches.
Immunotherapy Advancements
Immunotherapy, a groundbreaking field in cancer treatment, has shown promising results in both adult and pediatric melanoma cases. Harnessing the body’s immune system to target and eliminate cancer cells, immunotherapy is undergoing refinement for pediatric applications, with ongoing clinical trials exploring its efficacy and safety in younger populations.
Collaborative Initiatives
Global collaborative efforts are crucial in advancing research and treatment options for pediatric melanoma. Research consortia and international collaborations bring together experts from various fields to pool resources, share insights, and accelerate progress. These collaborative networks facilitate the development of standardized protocols for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care.
Psychosocial Support for Families
Coping with a pediatric cancer diagnosis, including melanoma, is undoubtedly challenging for families. Recognizing the emotional and psychological impact on children and their parents, healthcare professionals are increasingly incorporating psychosocial support services into comprehensive care plans. These services aim to address the emotional well-being of both the child and their family, fostering resilience and coping strategies.
Awareness Campaigns and Education
Raising awareness about pediatric melanoma is an ongoing priority. Public health campaigns and educational initiatives target parents, teachers, and healthcare providers to enhance awareness of risk factors, early signs, and preventive measures. These campaigns also emphasize the importance of regular check-ups and prompt medical attention for any concerning skin changes in children.
Navigating Survivorship
Survivorship care is a critical aspect of pediatric melanoma management. Long-term follow-up plans, tailored to the individual needs of each child, focus on monitoring for recurrence, managing potential treatment-related side effects, and supporting the child’s overall health and development. Survivorship programs also provide resources for transitioning into adulthood, ensuring continuity of care and support.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the field of pediatric melanoma research is poised for continued advancements. Integrating technological innovations, such as artificial intelligence for image analysis and early detection, holds promise in enhancing diagnostic precision. Additionally, personalized medicine approaches, guided by genetic profiling, may revolutionize treatment strategies for individualized care.
Empowering Communities and Advocacy
Community engagement and advocacy are integral to the broader effort to combat pediatric melanoma. Empowering communities with knowledge about risk factors and prevention, as well as fostering a supportive environment for affected families, strengthens the collective response to this health challenge.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the role of genetic factors in pediatric melanoma and explore how advancements in genomic research are shaping more targeted and effective treatment approaches for young patients.
Genetic Insights and Targeted Therapies: Paving the Way Forward
Genetic Factors in Pediatric Melanoma
As our understanding of pediatric melanoma deepens, the role of genetic factors has come to the forefront. Research has identified specific genetic mutations that may increase a child’s susceptibility to melanoma. The exploration of these genetic markers not only aids in early detection but also lays the foundation for targeted therapies designed to address the unique genetic profile of each patient.
Personalized Treatment Approaches
The emergence of targeted therapies marks a paradigm shift in pediatric melanoma treatment. By honing in on the genetic alterations driving the cancer, these therapies aim to disrupt specific pathways responsible for tumor growth. This personalized approach holds the promise of improved efficacy while potentially minimizing side effects compared to traditional treatments.
The Road Ahead: Integrating Technology and Precision Medicine
Technological advancements are playing a pivotal role in the ongoing battle against pediatric melanoma. Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for image analysis and early detection are on the horizon, offering a more refined and rapid means of identifying suspicious lesions. Integrating precision medicine into the standard of care involves tailoring treatments based on the genetic makeup of each patient, ushering in a new era of targeted and effective therapies.
Empowering Families and Communities
Empowering families with knowledge about pediatric melanoma is a crucial aspect of prevention and early intervention. Community awareness campaigns not only educate parents and caregivers about the signs and risk factors but also destigmatize discussions around childhood cancer. By fostering a supportive community environment, affected families can navigate the challenges of a pediatric melanoma diagnosis with resilience and strength.
In Conclusion
The landscape of pediatric melanoma is evolving, with advancements in research, diagnosis, and treatment offering hope for improved outcomes. Early detection remains paramount, and parents should stay vigilant for any changes in their child’s skin, promptly seeking medical attention if concerns arise.
As we look toward the future, collaborative efforts between researchers, healthcare professionals, and advocacy groups will continue to drive progress. Genetic insights are unraveling the complexities of melanoma, paving the way for personalized treatment approaches that hold great promise for the youngest members of our communities.
Education and awareness are our allies in the fight against pediatric melanoma. By fostering a culture of skin health and proactive healthcare practices, we can contribute to a future where this formidable challenge is met with resilience, innovation, and compassionate support for the affected children and their families.
In the chapters ahead, we will delve deeper into specific genetic markers associated with pediatric melanoma and explore the cutting-edge research shaping the landscape of targeted therapies for children facing this diagnosis. Understanding the molecular intricacies of the disease is a crucial step toward unlocking more effective and tailored treatment options.
Next Steps
If you find this information beneficial and wish to stay updated on children’s health topics, consider subscribing to our newsletter. If you’re concerned about any skin changes in your child, feel free to book an appointment with Dr. Michael Nwaneri. We’re here to offer expert advice, no obligations.