Laryngitis: The Unspoken Reality
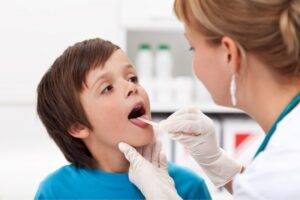
Laryngitis is often brushed off as a minor inconvenience, but when it strikes a child, the concern can be more significant. Let’s explore this condition that can temporarily rob your child of their voice.
What is Laryngitis?
Laryngitis is the inflammation of the voice box, or larynx, often resulting from overuse, irritation, or infection. It can lead to voice changes, such as hoarseness or even temporary loss of voice.
The Culprits: What Causes It?
Several factors can contribute to laryngitis:
- Viral Infections: Such as the common cold or flu.
- Vocal Strain: Yelling or excessive talking can be triggers.
- Allergies: Pollen, dust, or pet dander can irritate the larynx.
- Environmental Factors: Like smoke or chemical fumes.
Other Conditions Affecting the Head, Neck, and Nervous System
Understanding the conditions that affect the head, neck, and nervous system can help you identify symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment. Here are some key issues to be aware of:
1. Neurological Disorders
- Migraines: Severe headaches often accompanied by nausea, dizziness, and visual disturbances.
- Epilepsy: A condition characterized by recurrent seizures due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): A chronic illness involving damage to the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
2. Congenital Disorders
- Cerebral Palsy: A group of disorders affecting movement and muscle tone, caused by damage to the developing brain.
- Spina Bifida: A birth defect where there is incomplete closing of the backbone and membranes around the spinal cord.
3. Infections
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, often due to infection.
- Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain itself, commonly caused by viral infections.
4. Traumatic Injuries
- Concussions: Brain injuries resulting from impacts to the head, leading to temporary loss of normal brain function.
- Neck Injuries: Damage to the soft tissues or vertebrae in the neck, often due to accidents.
5. Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Parkinson’s Disease: A disorder that affects movement, causing tremors, stiffness, and slow movement.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: A progressive disease that destroys memory and other important mental functions.
6. Tumors
- Brain Tumors: Abnormal growths of cells in the brain which can be benign or malignant.
- Neck Tumors: Abnormal growths that can occur in the tissues of the neck, potentially affecting nearby structures.
7. Developmental Issues
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): A developmental disorder that affects communication and behavior.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A neurological condition marked by persistent inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness.
8. Other Conditions
- Thyroid Disorders: Conditions affecting the thyroid gland, located in the neck, which can influence metabolism, energy levels, and overall health.
- Bell’s Palsy: A condition causing sudden, temporary weakness in the muscles on one side of the face.
Prevention and Early Detection
Always consult with healthcare providers for early detection and management of these conditions as they are also serious and could be life-threatening.
Symptoms: More Than Just a Raspy Voice
While a hoarse voice is the hallmark symptom, others may include:
- Dry Throat: A scratchy or dry sensation.
- Sore Throat: Often accompanies the hoarseness.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Due to the inflamed larynx.

Diagnosis: How It’s Confirmed
The diagnosis usually involves:
- Physical Examination: Checking the throat and neck.
- Voice Tests: To assess the level of hoarseness.
- Endoscopy: In severe or persistent cases.
Treatment: Restoring the Voice
Treatment often focuses on symptom relief:
- Voice Rest: Limiting talking or singing.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids.
- Humidifiers: To add moisture to the air.
- Medication: Antibiotics for bacterial infections.

Emotional Impact: The Silent Struggle
Losing the ability to speak, even temporarily, can be frustrating for a child. Emotional support and alternative communication methods can help during this period.
Prevention: Keeping the Voice Box Healthy
Simple steps like staying hydrated, avoiding smoke, and not straining the voice can go a long way in prevention.
Next Steps
If you find this information beneficial and wish to stay updated on children’s health topics, consider subscribing to our newsletter. If you’re dealing with laryngitis or other vocal issues in your child, feel free to book an appointment with Dr. Michael Nwaneri. We’re here to offer expert advice, no obligations.