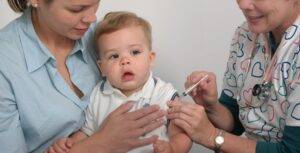
Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). This virus specifically targets the liver, leading to both acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) liver diseases. If left untreated, it can progress to severe conditions such as cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) and hepatocellular carcinoma (a type of liver cancer).
The virus is highly contagious and transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, and other bodily fluids. Infants and young children are especially vulnerable to the disease, and the infection has severe and long-lasting effects on their health.
Why Hepatitis B is a Major Concern
Hepatitis B is a global health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 257 million people are living with the chronic infection, causing about 887,000 deaths annually, primarily due to liver complications.
The virus is transmitted from mother to child during childbirth, through blood transfusions, and by sharing needles or other sharp instruments. In children, the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is much higher compared to adults, making early prevention crucial.
The Hepatitis B Vaccine: A Lifesaver
The vaccine is a powerful tool in the fight against the disease. It is safe, effective, and has been instrumental in reducing the incidence of the disease worldwide. The vaccine is typically administered in three to four shots over six months.
It works by stimulating the body’s immune system to produce antibodies that can fight off the virus if the person is exposed in the future.
How the Vaccine Works
The vaccine contains a small part of the virus (not live) and is sufficient to stimulate an immune response without causing the disease.
When vaccinated, the body recognizes this component as foreign and produces antibodies to fight it off. These antibodies remain in the body and provide long-term protection against the virus.
Benefits of the Hepatitis B Vaccine
- Prevents Chronic Infection: Vaccination at birth significantly reduces the risk of chronic infection, which can lead to severe liver diseases later in life.
- Protects Against Liver Cancer: By preventing chronic infection, the vaccine reduces the risk of liver cancer.
- Reduces Transmission Rates: Widespread vaccination helps decrease the overall prevalence of the disease, making the community safer.
- Cost-Effective: Preventing the disease through vaccination is far more cost-effective than treating chronic liver diseases and cancer associated with the infection.
Vaccination Schedule for Children
Birth Dose
The first dose of the vaccine is administered within 24 hours of birth. This “birth dose” is crucial for preventing mother-to-child transmission of the virus. Babies born to mothers who are hepatitis B positive are at high risk, so the birth dose is an important protective measure.
Follow-Up Doses
After the birth dose, children receive additional doses of the vaccine at 1-2 months and 6-18 months of age. This schedule ensures the child develops a strong and lasting immunity against the virus.
Importance of Completing the Vaccine Series
Complete the full series of vaccinations to ensure maximum protection. Incomplete vaccination leaves children vulnerable to infection. Parents should follow the vaccination schedule recommended by healthcare providers and keep track of their child’s immunization records.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers are on the front lines of the fight against hepatitis B. They play a critical role in:
- Administering Vaccines: Ensuring children receive the vaccine according to the recommended schedule.
- Educating Families: Providing information and support to parents about the importance of vaccination and addressing any concerns.
- Monitoring Health: Keeping vaccination records and following up with families to ensure children complete the vaccine series.
Building Trust with Families
Trust between healthcare providers and families is essential for successful vaccination programs. Providers should build relationships with families, listen to their concerns, and provide reliable information about the benefits and safety of vaccines. By fostering trust, providers can help increase vaccine acceptance and coverage.
Staying Informed
Healthcare providers should stay informed about the latest research and guidelines related to vaccination. Keeping up-to-date with current information allows providers to give accurate advice and address any new concerns.
Overcoming Vaccine Hesitancy
Despite the proven benefits of the hepatitis B vaccine, some parents may hesitate to vaccinate their children due to misconceptions or fears about vaccine safety. It is essential to address these concerns with accurate information and reassure parents about the safety and importance of the hepatitis B vaccine.
Common Misconceptions
- Vaccine Safety: The hepatitis B vaccine has been thoroughly tested and monitored for safety. Serious side effects are rare, and the benefits far outweigh the risks.
- Necessity: Some parents believe their child is not at risk for hepatitis B, but the virus spreads in many ways, including through household contacts and minor injuries.
- Effectiveness: The hepatitis B vaccine is highly effective, with a success rate of about 95% in preventing infection when the full vaccine series is completed.
Educating Parents
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating parents about the importance of the hepatitis B vaccine. Providing clear, evidence-based information and addressing any questions or concerns help parents make informed decisions about vaccinating their children.
Communicating with Empathy
When discussing vaccinations with hesitant parents, healthcare providers communicate with empathy and understanding. Listening to parents’ concerns, providing factual information, and sharing personal experiences help build trust and encourage vaccine acceptance.
Addressing Barriers to Vaccination
Several barriers can hinder the uptake of the hepatitis B vaccine, including logistical, financial, and social factors. Addressing these barriers is essential for improving vaccination rates and protecting children’s health.
Logistical Barriers
In some areas, access to healthcare facilities and vaccines can be limited. Mobile vaccination clinics, community outreach programs, and partnerships with local organizations help overcome logistical barriers and ensure children’s access to the hepatitis B vaccine.
Financial Barriers
The cost of vaccines is a significant barrier for some families. Governments and international organizations work to provide funding and support to make vaccines affordable and accessible. Programs, like the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (GAVI) provide vaccines to low-income countries.
Social Barriers
Cultural beliefs and misinformation can also hinder vaccination efforts. Community leaders, educators, and healthcare providers should work together to address these social barriers. Public awareness campaigns, educational programs, and community engagement can help dispel myths and promote the importance of vaccination.
The Impact of Hepatitis B Vaccination
Hearing personal stories from individuals and families affected by hepatitis B underscores the importance of vaccination. These stories provide a powerful reminder of the real-life impact of hepatitis B and the critical role that vaccines play in preventing this disease.
The Role of Advocacy
Advocacy efforts by individuals, healthcare providers, and organizations are essential in promoting hepatitis B vaccination. Raising awareness, advocating for policy changes, and supporting vaccination programs ensure that all children receive the protection they need against hepatitis B.
The Impact of Vaccination Programs
Widespread hepatitis B vaccination programs have a significant impact on public health. In countries with high vaccination coverage,
the incidence of hepatitis B has dropped dramatically, leading to lower rates of chronic liver disease and liver cancer. These programs demonstrate the power of vaccination in controlling and eventually eradicating infectious diseases.
Global Success Stories
Countries like Taiwan and South Korea have implemented successful hepatitis B vaccination programs that drastically reduced the incidence of hepatitis B in their populations. These programs serve as models for other countries working to eliminate hepatitis B as a public health threat.
Ongoing Challenges
Despite the success of vaccination programs, challenges remain in reaching all children, especially in low-resource settings. Efforts to improve vaccine access, educate communities, and strengthen healthcare systems are essential to ensuring that every child receives the hepatitis B vaccine.
Importance of Global Cooperation
Global cooperation and support are vital in the fight against hepatitis B. International organizations, governments, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) work together to provide funding, resources, and technical assistance to countries.
By sharing knowledge and expertise, the global community makes significant strides toward eliminating hepatitis B.
The Long-Term Benefits of Hepatitis B Vaccination
The benefits of hepatitis B vaccination extend beyond individual health. Widespread vaccination helps protect communities, reduce healthcare costs, and contribute to global health goals.
Herd Immunity
When a high percentage of the population is vaccinated, it creates herd immunity. This means that even those not vaccinated, such as newborns or individuals with certain medical conditions, are less likely to be exposed to the virus. Herd immunity is essential for protecting vulnerable populations and preventing outbreaks.
Reducing Healthcare Costs
Preventing hepatitis B through vaccination is far more cost-effective than treating chronic liver diseases and liver cancer associated with the infection. Vaccination reduces the burden on healthcare systems, allowing allocation of resources to other critical health needs.
Contributing to Global Health Goals
Hepatitis B vaccination is a key component of global health initiatives to reduce infectious diseases and improve overall health. By achieving high vaccination coverage, countries make significant progress toward global health targets, such as the WHO’s goal of eliminating viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030.
The Role of Parents in Preventing Hepatitis B
Parents play a crucial role in protecting their children from hepatitis B. By staying informed about the vaccine, following the recommended vaccination schedule, and advocating for vaccination, parents ensure their children are protected from this serious infection.
Keeping Track of Vaccinations
Parents keep accurate records of their children’s vaccinations and ensure they receive all doses on time. Tools such as vaccination reminder apps or keeping a written record help parents stay organized and up-to-date with their child’s immunization schedule.
Advocating for Vaccination
Parents can advocate for vaccination within their communities. By sharing their positive experiences, dispelling myths, and encouraging others to vaccinate their children, parents increase vaccination rates and protect more children from hepatitis B.
Staying Informed
Staying informed about the latest research and recommendations related to hepatitis B vaccination is important. Trusted sources such as healthcare providers, public health organizations, and reputable websites provide accurate and up-to-date information.
The Future of Hepatitis B Prevention
Advancements in vaccine technology and public health strategies continue to improve the effectiveness and accessibility of hepatitis B vaccination programs. Ongoing research and innovation are essential for achieving long-term success in preventing hepatitis B.
New Vaccine Developments
Researchers are continually working on developing new vaccines and improving existing ones. Innovations such as combination vaccines, which protect against multiple diseases with a single shot, can simplify vaccination schedules and increase coverage.
Digital Health Solutions
Digital health technologies, such as electronic health records and mobile health applications, improve vaccination tracking and reminders. These tools ensure that children receive all doses on time and that healthcare providers monitor vaccination coverage more effectively.
Strengthening Public Health Systems
Strong public health systems are crucial for the successful implementation of vaccination programs. Investments in healthcare infrastructure, training for healthcare workers, and robust surveillance systems enhance the delivery and monitoring of vaccines.
Additionally, partnerships with local communities and organizations ensure that vaccination programs are tailored to meet the needs of different populations.
Give Hepatitis B Vaccine for Your Child’s Protection
The hepatitis B vaccine is a cornerstone of childhood immunization programs worldwide. It’s a safe, effective, and cost-efficient way to protect children from a potentially life-threatening disease.
By preventing hepatitis B infection, the vaccine helps reduce the burden of chronic liver disease and liver cancer, ultimately saving lives and improving public health. Ensuring children receive the hepatitis B vaccine is essential for a healthier future.
For more information on pediatric health and vaccination, visit Omega Pediatrics and read our articles on
- Why Hepatitis B is Crucial for Children: Essential Ages for Immunization
- Immunization: The Shield Against Preventable Diseases
By supporting and promoting hepatitis B vaccination, we protect our children from this dangerous virus and work towards a world free of hepatitis B. Through education, advocacy, and global cooperation, we ensure that every child has the opportunity to grow up healthy and hepatitis B-free.