Childhood asthma is a prevalent condition affecting approximately 6 million children in the United States, which accounts for 1 in 12 children. The impact of asthma on children’s daily activities can be significant, leading to various challenges that affect their quality of life, social interactions, and overall health.
How asthma can affect a child’s daily activities:
- Physical activity: Asthma can limit a child’s ability to engage in physical activities and sports due to exercise-induced symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
- School attendance: Asthma flare-ups and symptoms may lead to missed school days, affecting a child’s regular attendance, academic progress, and social interactions with peers.
- Social activities: Children with asthma may face limitations in participating in certain social activities, such as outdoor events, camps, or playdates, to avoid triggers that can worsen their symptoms.
- Sleep: Asthma symptoms can disrupt a child’s sleep patterns, causing nighttime coughing, wheezing, or difficulty breathing, which can lead to fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and impaired concentration.
- Emotional well-being: Asthma can have emotional and psychological effects on children, including anxiety, frustration, and a sense of isolation due to their condition and the need to manage it.
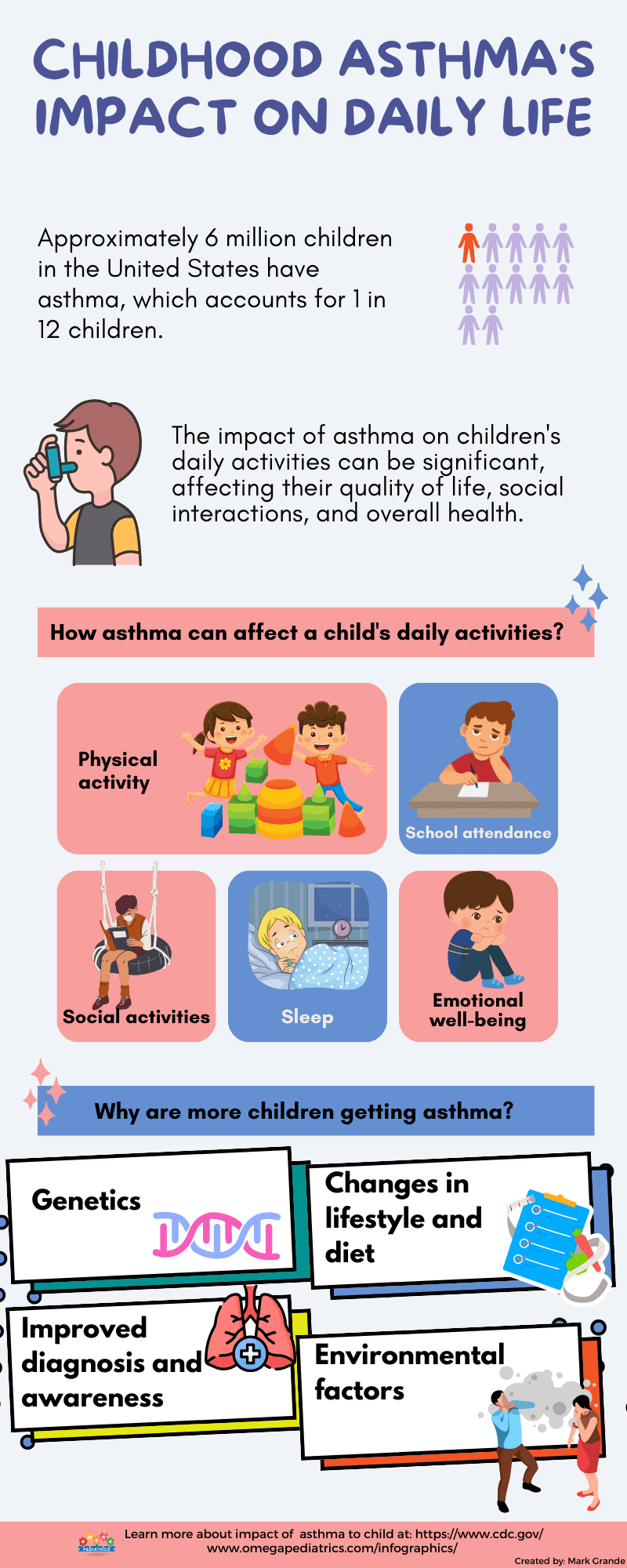
Why are more children getting asthma:
- Genetics: Family history of asthma or allergies can increase the likelihood of a child developing asthma, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Changes in lifestyle and diet: Environmental changes, sedentary lifestyles, increased exposure to indoor allergens, pollution, and dietary factors have been associated with the rising prevalence of asthma in children.
- Improved diagnosis and awareness: Increased awareness and better diagnostic techniques have led to improved identification and diagnosis of asthma cases that might have gone undetected in the past, resulting in higher reported rates.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to environmental triggers such as air pollution, secondhand smoke, allergens (such as dust mites, pollen, and pet dander), and respiratory infections can contribute to the development and exacerbation of asthma in children.
Understanding the impact of asthma on children’s daily lives and the factors contributing to its prevalence helps in developing effective strategies for prevention, management, and support. By promoting awareness, providing appropriate medical care, creating asthma-friendly environments, and empowering children and their families with proper education and resources, we can strive to improve the quality of life for children with asthma and reduce the burden of this chronic condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of childhood asthma reverberates through various aspects of a child’s daily life, from physical activities to social interactions and emotional well-being. The limitations posed by asthma, including restricted participation in sports, missed school days, and altered sleep patterns, highlight the need for a holistic approach to managing this prevalent condition.
As we explore the factors contributing to the rise in childhood asthma cases, it becomes evident that a combination of genetic predisposition, lifestyle changes, and improved diagnostic awareness plays a role. Recognizing these influencers enables us to develop targeted strategies for prevention, management, and support.
Creating asthma-friendly environments, fostering awareness, and providing proper medical care are integral components of a comprehensive approach to improving the lives of children with asthma. Empowering both children and their families with education and resources not only aids in managing the condition but also enhances their ability to navigate the challenges posed by asthma on a daily basis.
In our collective efforts to mitigate the impact of childhood asthma, we strive to create a world where every child can breathe freely, engage fully in life’s activities, and thrive despite the challenges of this chronic condition.