Table of Contents
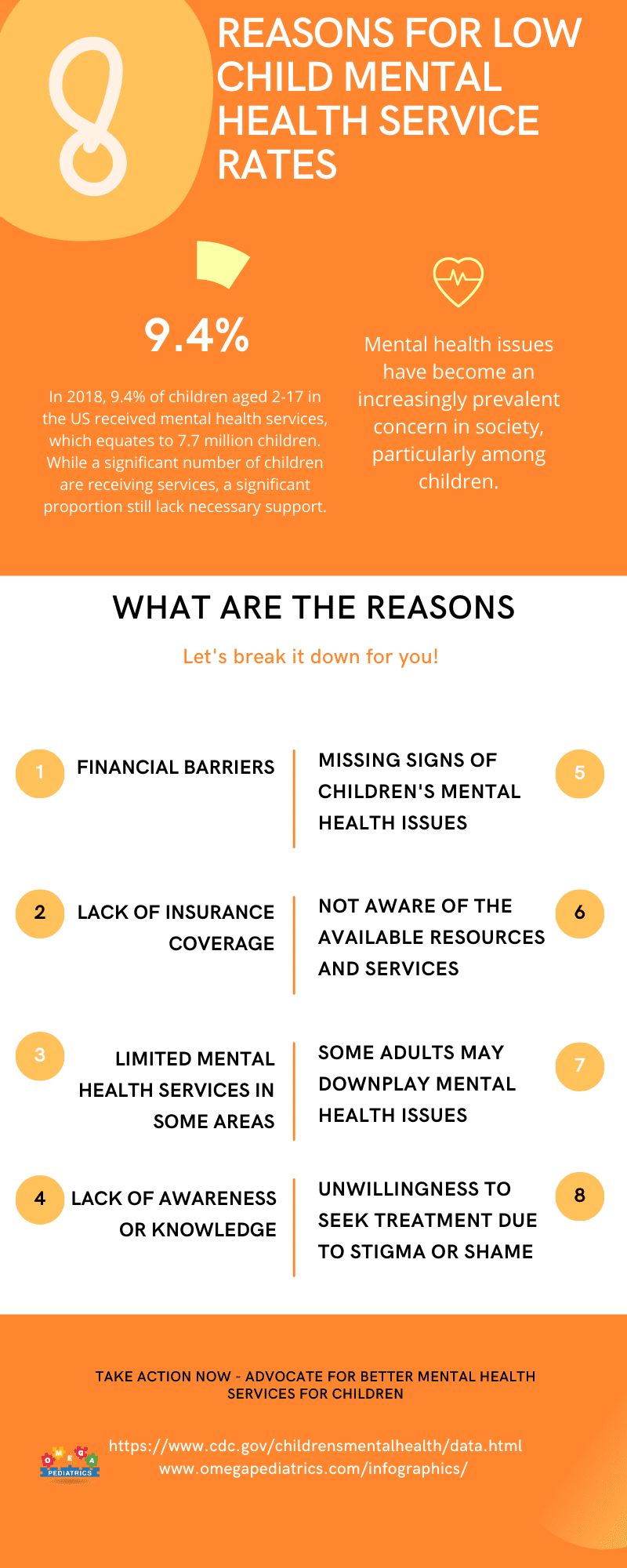
In 2018, 9.4% of children aged 2-17 in the US received mental health services, which equates to 7.7 million children. While a significant number of children are receiving services, a considerable proportion still lack the necessary support, highlighting the existing gap in access to child mental health services.
Mental health issues have become an increasingly prevalent and pressing concern in society, particularly among children. Despite this growing recognition, several factors contribute to the low rates of child mental health service utilization, hindering the ability of children in need to access appropriate care.
- Financial barriers: Financial constraints that hinder access to mental health services for children and their families.
- Lack of insurance coverage: Insufficient or no insurance coverage for mental health services, making it difficult for families to afford necessary treatment.
- Limited mental health services in some areas: Inadequate availability or accessibility of mental health services in certain geographic regions, limiting the options for families seeking care.
- Lack of awareness or knowledge: Insufficient understanding or awareness among parents and caregivers about the importance of mental health, its impact on children, and available services for support and treatment.
- Missing signs of children’s mental health issues: Failure to recognize or identify signs and symptoms of mental health problems in children, leading to delayed intervention and treatment.
- Not aware of the available resources and services: Lack of knowledge about the existence and availability of mental health resources, support groups, therapy services, or community programs that can provide assistance to children and their families.
- Some adults may downplay mental health issues: A tendency among some adults to minimize or dismiss mental health concerns in children, attributing them to normal behavior or temporary phases, thereby delaying or avoiding seeking professional help.
- Unwillingness to seek treatment due to stigma or shame: Negative attitudes, societal stigma, or feelings of shame associated with mental health problems, which may discourage parents and caregivers from seeking treatment for their children due to fear of judgment or discrimination.
Understanding these factors helps in recognizing the barriers that prevent children from receiving the necessary mental health services. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive efforts to increase awareness, improve accessibility, reduce stigma, and promote early intervention and treatment for children’s mental health issues.
Breaking Down Barriers: Why Child Mental Health Service Rates Remain Low
In an era where mental health awareness is on the rise, it’s disconcerting that a significant number of children still lack access to essential mental health services. The low utilization rates, as indicated by the 2018 statistics revealing that only 9.4% of children aged 2-17 in the US received mental health services, underscore the existing gap in addressing the mental health needs of our youth.
1. Financial Barriers:
One of the primary obstacles to accessing child mental health services is financial constraints. Many families face challenges affording the necessary care, creating a significant barrier for children in need. Addressing this issue requires not only increased funding for mental health services but also a broader societal understanding of the long-term benefits of investing in the mental well-being of our youth.
2. Lack of Insurance Coverage:
Insufficient or absent insurance coverage for mental health services is a critical factor contributing to low service rates. Families struggling with financial limitations find it particularly challenging to afford the necessary treatment. Advocating for expanded insurance coverage for mental health services is crucial to ensuring that financial considerations do not hinder children from receiving the care they require.
3. Limited Availability in Some Areas:
Geographic disparities in the availability of mental health services pose a significant challenge. In certain regions, there is inadequate access to mental health resources, limiting the options for families seeking assistance. Addressing this issue involves strategic planning to enhance the distribution of mental health services and resources across diverse communities.
4. Lack of Awareness or Knowledge:
Insufficient understanding or awareness about the importance of mental health in children remains a critical hurdle. Parents and caregivers need to be educated on the impact of mental health on children and the available services for support and treatment. Community outreach programs and educational initiatives can play a pivotal role in disseminating this crucial information.
5. Missing Signs of Mental Health Issues:
Failure to recognize or identify signs and symptoms of mental health problems in children contributes to delayed intervention and treatment. Increasing awareness among parents, teachers, and healthcare providers about the early indicators of mental health issues is essential for timely and effective support.
6. Unawareness of Available Resources:
A lack of knowledge about existing mental health resources and services further hinders families. Awareness campaigns and community programs can bridge this information gap, ensuring that families know where to turn for assistance, therapy services, and support groups.
7. Adult Minimization of Mental Health Issues:
Some adults may downplay mental health concerns in children, attributing them to normal behavior or passing phases. This tendency delays or even prevents seeking professional help. Raising awareness about the nuanced nature of mental health in children is crucial to dispel misconceptions and promote early intervention.
8. Stigma and Shame:
Negative attitudes, societal stigma, and feelings of shame associated with mental health problems contribute to a reluctance to seek treatment. Combatting this stigma requires a collective effort to foster a more compassionate and understanding society. Advocacy campaigns and destigmatization initiatives can create an environment where seeking help is seen as a sign of strength rather than weakness.
Understanding these multifaceted factors that contribute to low child mental health service rates is the first step towards creating a more supportive and accessible system. By addressing these challenges through increased awareness, improved accessibility, reduced stigma, and promoting early intervention, we can work towards ensuring that every child has the opportunity to receive the mental health support they need.
FAQ
What are the primary obstacles to accessing child mental health services?
Financial constraints pose a significant barrier for many families, hindering their ability to afford necessary care for their children’s mental health.
Why do some families struggle to afford mental health treatment for their children?
Insufficient or absent insurance coverage for mental health services makes it challenging for families facing financial limitations to access the necessary treatment.
What geographic challenge contributes to low child mental health service rates?
Limited availability of mental health services in certain regions creates barriers for families seeking assistance, highlighting the need for strategic planning to enhance distribution across diverse communities.
What is a crucial factor in addressing low awareness about child mental health issues?
Educating parents and caregivers about the impact of mental health on children and available support and treatment services is essential for increasing awareness and understanding.
What contributes to delayed intervention and treatment for children’s mental health issues?
Failure to recognize or identify signs and symptoms of mental health problems in children leads to delayed intervention and treatment, emphasizing the importance of increasing awareness among parents, teachers, and healthcare providers.