Table of Contents
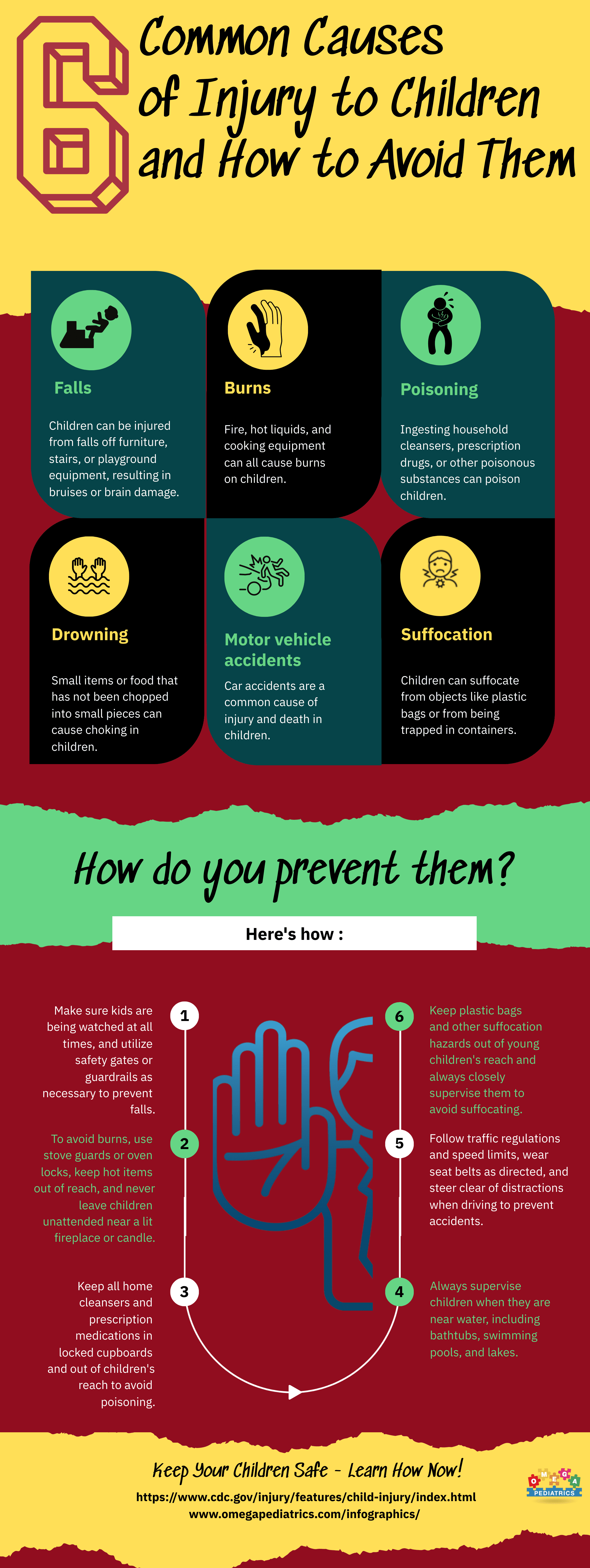
The most common causes of injury-related deaths among children vary depending on their age and developmental stage. However, some of the most common causes of injury-related deaths among children are drowning, motor vehicle accidents, suffocation, poisoning, falls, and burns.
Here are some ways to prevent each of these types of injuries:
- Drowning: Children should be supervised at all times when they are near water, including bathtubs, swimming pools, and lakes. Pools should be surrounded by a fence with a self-latching gate, and children should be taught to swim as early as possible.
- Motor vehicle accidents: Children should always wear a seatbelt or be secured in a child safety seat appropriate for their age and size. Parents should also avoid distracted driving, never leave children unattended in a vehicle, and teach children to never play near or in the street.
- Suffocation: Infants should always sleep on their backs on a firm, flat surface with no loose bedding, soft objects, or bumpers in the crib. Parents should also keep plastic bags, balloons, and other choking hazards out of reach of children.
- Poisoning: Medications and household cleaning products should be stored in their original containers and out of reach of children. Parents should also teach children not to touch or ingest anything that is not food or drink.
- Falls: Children should always be supervised when playing on playgrounds, climbing on furniture, or walking on uneven surfaces. Windows should also have safety bars or window guards to prevent falls.
- Burns: Children should be kept away from hot objects such as stoves, ovens, and fireplaces. Parents should also set their water heaters to no higher than 120 degrees Fahrenheit to prevent scalding and teach children about the dangers of playing with matches and lighters.
Overall, prevention of injury-related deaths in children requires a combination of parental supervision, education, and environmental modifications. By taking these steps, parents can help ensure the safety and well-being of their children.
How do you prevent them?
To prevent injury-related deaths in children, there are several steps that parents and caregivers can take. Here are some specific strategies for preventing each of the most common causes of injury-related deaths in children:
Drowning: Always supervise children when they are near water, including bathtubs, swimming pools, and lakes. Pools should be surrounded by a fence with a self-latching gate, and children should be taught to swim as early as possible.
Motor vehicle accidents: Always use a seatbelt or child safety seat appropriate for the child’s age and size. Avoid distracted driving, never leave children unattended in a vehicle, and teach children to never play near or in the street.
Suffocation: Infants should always sleep on their backs on a firm, flat surface with no loose bedding, soft objects, or bumpers in the crib. Keep plastic bags, balloons, and other choking hazards out of reach of children.
Poisoning: Store medications and household cleaning products in their original containers and out of reach of children. Teach children not to touch or ingest anything that is not food or drink.
Falls: Always supervise children when playing on playgrounds, climbing on furniture, or walking on uneven surfaces. Install safety gates at the top and bottom of stairs, and windows should have safety bars or window guards to prevent falls.
Burns: Keep children away from hot objects such as stoves, ovens, and fireplaces. Set water heaters to no higher than 120 degrees Fahrenheit to prevent scalding, and teach children about the dangers of playing with matches and lighters.
Overall, preventing injury-related deaths in children requires a combination of parental supervision, education, and environmental modifications. By taking these steps, parents and caregivers can help ensure the safety and well-being of their children.
Understanding and Preventing Common Causes of Childhood Injuries
Childhood is a time of exploration and discovery, but it comes with inherent risks. Parents and caregivers must be vigilant in understanding and addressing the common causes of injury-related deaths among children. Let’s delve deeper into each cause and explore effective prevention strategies.
1. Drowning:
Drowning remains a leading cause of injury-related deaths in children. To prevent such tragedies, constant supervision is paramount. Whether near bathtubs, swimming pools, or lakes, children should always be closely monitored. Installing a fence with a self-latching gate around pools adds an extra layer of protection. Equally crucial is early swimming education, empowering children with essential water safety skills.
2. Motor Vehicle Accidents:
Motor vehicle accidents pose a significant risk to child safety. Ensuring that children always wear seatbelts or are secured in age-appropriate safety seats is non-negotiable. Parents can contribute to safety by avoiding distracted driving, never leaving children unattended in a vehicle, and instilling a strong understanding in children about the dangers of playing near or in the street.
3. Suffocation:
For infants, the risk of suffocation is a concern during sleep. Placing infants on their backs on a firm, flat surface devoid of loose bedding, soft objects, or bumpers in the crib is a critical practice. Additionally, keeping plastic bags, balloons, and other choking hazards out of children’s reach is essential for a safe environment.
4. Poisoning:
Preventing poisoning involves secure storage of medications and household cleaning products in their original containers and out of reach of children. Education plays a vital role as well, with parents teaching children not to touch or ingest anything that isn’t explicitly designated as food or drink.
5. Falls:
Children’s natural curiosity often leads to climbing and exploring, making falls a common concern. Supervision during play on playgrounds, climbing on furniture, and walking on uneven surfaces is crucial. Installing safety gates at the top and bottom of stairs and implementing window guards or safety bars can significantly reduce the risk of falls.
6. Burns:
Burns can result from contact with hot objects like stoves, ovens, and fireplaces. Parents can mitigate this risk by keeping children away from these sources of heat. Setting water heaters to a maximum of 120 degrees Fahrenheit prevents scalding, while educating children about the dangers of matches and lighters enhances their awareness.
Preventing Childhood Injuries: A Holistic Approach
In summary, preventing injury-related deaths in children requires a holistic approach encompassing parental supervision, education, and environmental modifications. By consistently implementing these preventative measures, parents and caregivers contribute to the safety and well-being of their children, fostering an environment where exploration and growth can occur with minimized risks.
FAQ
How can I prevent drowning incidents involving children?
Always supervise children near water, whether in bathtubs, pools, or lakes. Install fencing around pools with self-latching gates and ensure children learn to swim early.
What steps can I take to avoid motor vehicle accidents with children?
Ensure children use seatbelts or appropriate safety seats. Avoid distracted driving, never leave children alone in a vehicle, and educate them about the dangers of playing near roads.
How do I prevent suffocation risks for infants?
Place infants on their backs on a firm surface without loose bedding or objects in the crib. Keep plastic bags and choking hazards out of their reach.
What measures can I implement to prevent poisoning incidents?
Store medications and cleaning products securely and educate children about not touching or ingesting non-food items.
How can I reduce the risk of falls for children?
Supervise children during play, install safety gates at stairs, and use window guards to prevent falls from windows.