Table of Contents
The average age for children to start attending school varies by country and educational system. In many countries, children start attending primary school between the ages of five and seven.
In the United States, children typically start attending kindergarten at age five, although some states have a lower age requirement. Primary school, which is also called elementary school, usually lasts from grades 1-5 or 1-6, depending on the state. After primary school, children attend middle school or junior high school, which usually covers grades 6-8. High school covers grades 9-12, and students typically graduate at around age 18.
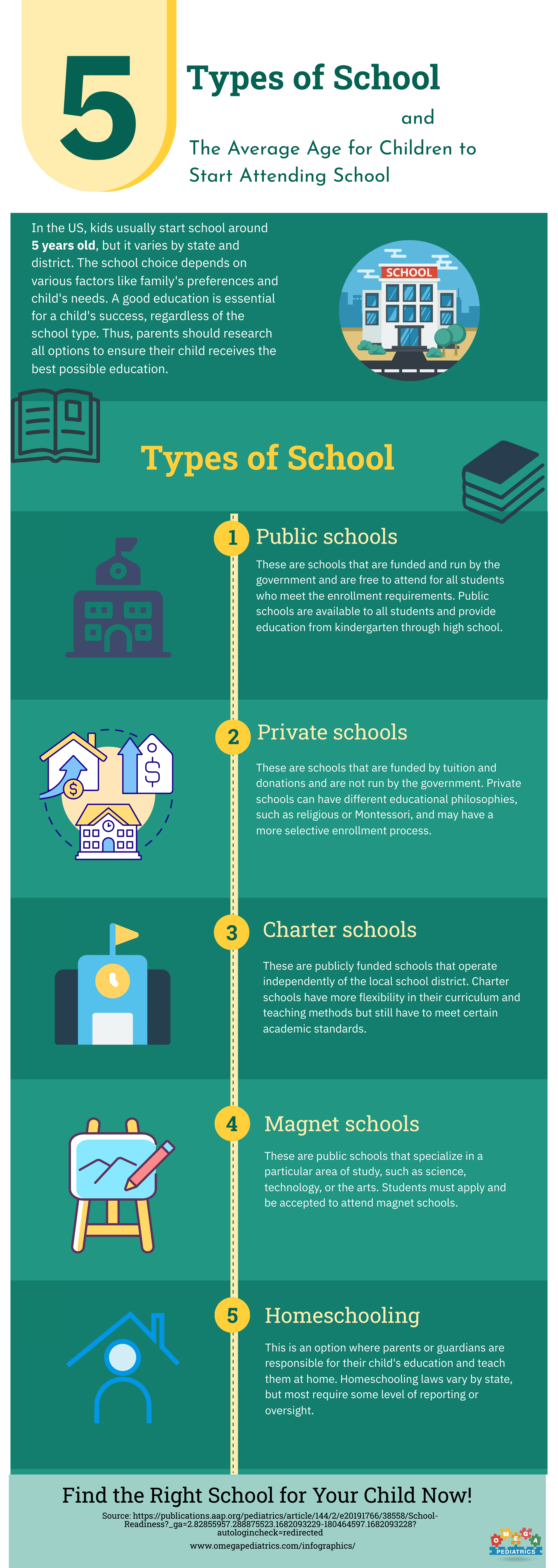
There are several different types of schools available, including public schools, private schools, charter schools, and homeschooling.
5 Types of School
Public Schools: These are schools that are funded and run by the government and are free to attend for all students who meet the enrollment requirements. Public schools are available to all students and provide education from kindergarten through high school.
Private Schools: These are schools that are funded by tuition and donations and are not run by the government. Private schools can have different educational philosophies, such as religious or Montessori, and may have a more selective enrollment process.
Charter Schools: These are publicly funded schools that operate independently of the local school district. Charter schools have more flexibility in their curriculum and teaching methods but still have to meet certain academic standards.
Magnet Schools: These are public schools that specialize in a particular area of study, such as science, technology, or the arts. Students must apply and be accepted to attend magnet schools.
Homeschooling: This is an option where parents or guardians are responsible for their child’s education and teach them at home. Homeschooling laws vary by state, but most require some level of reporting or oversight.
These are just a few of the many types of schools available. Each type of school has its own unique approach to education, and it’s important to choose the one that best fits your child’s learning style and needs.
The Importance of Early Education
While the average age for children to start attending school varies globally, the significance of early education is universally recognized. Early education plays a crucial role in a child’s cognitive, social, and emotional development. It sets the foundation for a lifelong love of learning and helps children acquire essential skills that will benefit them throughout their academic journey.
In the United States, the early education journey often begins with kindergarten, a term derived from the German language, meaning “children’s garden.” Kindergarten serves as an introduction to the structured learning environment and provides children with a social setting where they can interact with peers and learn valuable social skills.
Navigating the Educational Landscape
The American education system further unfolds as students progress through primary, middle, and high school. Primary school, also known as elementary school, forms the bedrock of a child’s academic experience. The subsequent transition to middle school or junior high school marks a period of increased academic rigor and personal growth.
High school, covering grades 9-12, is a pivotal phase where students delve into a diverse range of subjects, preparing for future academic pursuits or entering the workforce. Graduating from high school signifies not only the completion of a formal education but also the readiness to embark on the next chapter of life.
Diversity in Educational Options
Beyond the traditional trajectory, the educational landscape offers a variety of school types to cater to diverse learning preferences and philosophies. Public schools, funded by the government, ensure accessibility for all students. Private schools, on the other hand, provide alternative educational approaches and often have more selective admission processes.
Charter schools, a unique feature of the American educational system, combine public funding with increased autonomy. This autonomy allows them to experiment with innovative teaching methods and curricula while adhering to academic standards.
Magnet schools stand out for their specialized focus on specific areas of study, fostering a deep exploration of subjects like science, technology, or the arts. The competitive application process adds an element of selectivity to these institutions.
Empowering Parents: The Rise of Homeschooling
In recent years, homeschooling has gained popularity as an alternative educational option. Empowering parents to take an active role in their child’s education, homeschooling allows for personalized learning experiences. While laws governing homeschooling vary by state, many require parents to follow specific reporting or oversight procedures to ensure educational standards are met.
Choosing the Right Fit
As parents navigate the educational landscape, it’s essential to consider the unique needs and learning styles of their children. The array of educational options available allows for a tailored approach to learning, ensuring that each child has the opportunity to thrive in an environment that suits them best.
In conclusion, understanding the educational journey, from early childhood to high school graduation, empowers parents to make informed decisions about their children’s education. Whether opting for traditional public or private schools, exploring innovative charter or magnet schools, or embracing the flexibility of homeschooling, the diverse educational landscape in the United States offers a multitude of paths for students to embark upon as they grow and learn.
FAQ
What is the average age for children to start attending school in the United States?
In the United States, children typically start attending kindergarten at age five, although some states may have lower age requirements. Primary school, also known as elementary school, usually begins around age six or seven and lasts from grades 1-5 or 1-6, depending on the state.
What are the different types of schools available for children?
There are several types of schools available, including public schools, private schools, charter schools, magnet schools, and homeschooling. Each type of school offers unique approaches to education, catering to diverse learning styles and preferences.
What is the difference between public and private schools?
Public schools are funded and run by the government, providing free education to all students who meet enrollment requirements. Private schools, on the other hand, are funded by tuition and donations, offering alternative educational philosophies and often having a more selective enrollment process.
What are magnet schools, and what makes them unique?
Magnet schools are public schools that specialize in specific areas of study, such as science, technology, or the arts. Students must apply and be accepted to attend magnet schools, which offer a focused curriculum and immersive learning experiences in their chosen field.
What is homeschooling, and how does it work?
Homeschooling is an option where parents or guardians are responsible for their child’s education and teach them at home. Homeschooling laws vary by state, but most require some level of reporting or oversight to ensure educational standards are met. It allows for personalized learning experiences tailored to the child’s needs and preferences.